Connect to a TiDB Dedicated Cluster via Google Cloud Private Service Connect
This document describes how to connect to your TiDB Dedicated cluster via Google Cloud Private Service Connect. Google Cloud Private Service Connect is a private endpoint service provided by Google Cloud.
TiDB Cloud supports highly secure and one-way access to the TiDB Cloud service hosted in a Google Cloud VPC via the Private Service Connect. You can create an endpoint and use it to connect to the TiDB Cloud service .
Powered by Google Cloud Private Service Connect, the endpoint connection is secure and private, and does not expose your data to the public internet. In addition, the endpoint connection supports CIDR overlap and is easier for network management.
The architecture of the private endpoint is as follows:
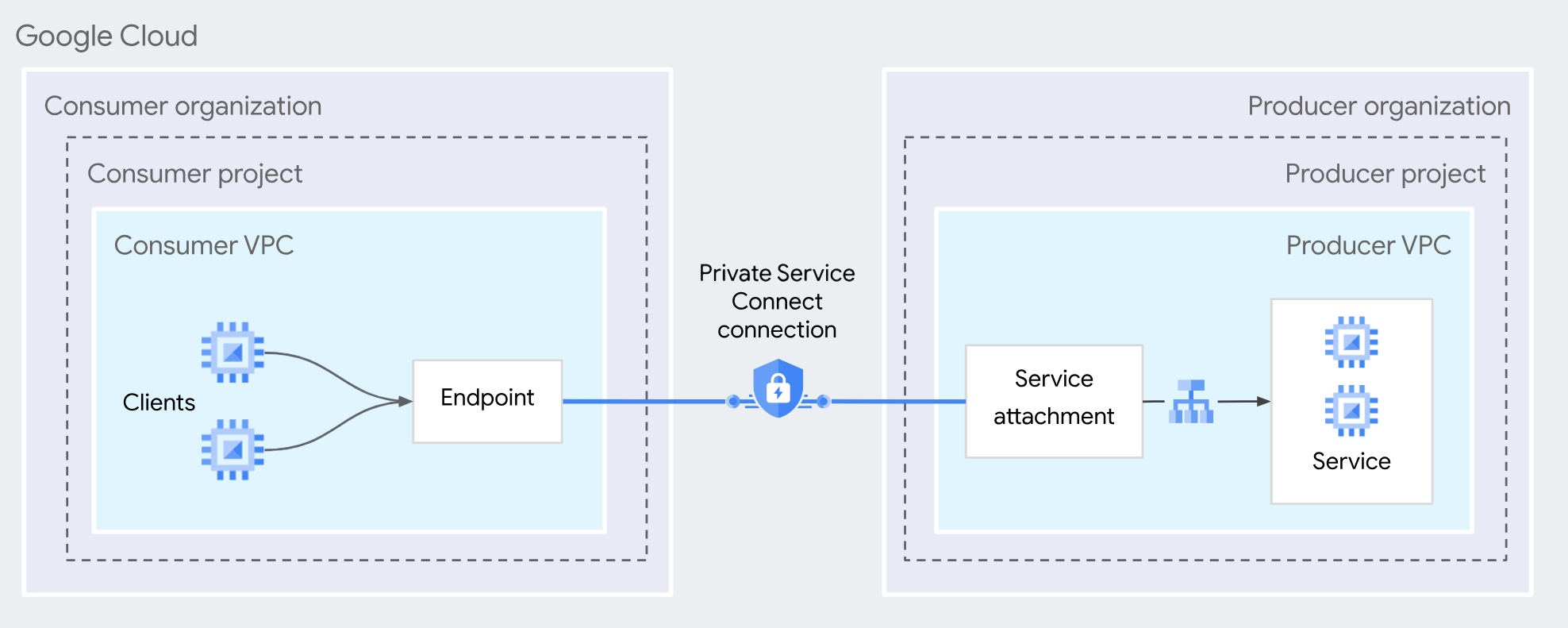
For more detailed definitions of the private endpoint and endpoint service, see the following Google Cloud documents:
Restrictions
- This feature is applicable to TiDB Dedicated clusters created after April 13, 2023. For older clusters, contact TiDB Cloud Support for assistance.
- Only the
Organization OwnerandProject Ownerroles can create Google Cloud Private Service Connect endpoints. - Each TiDB cluster can handle connections from up to 10 endpoints.
- Each Google Cloud project can have up to 10 endpoints connecting to a TiDB Cluster.
- You can create up to 8 TiDB Dedicated clusters hosted on Google Cloud in a project with the endpoint service configured.
- The private endpoint and the TiDB cluster to be connected must be located in the same region.
- Egress firewall rules must permit traffic to the internal IP address of the endpoint. The implied allow egress firewall rule permits egress to any destination IP address.
- If you have created egress deny firewall rules in your VPC network, or if you have created hierarchical firewall policies that modify the implied allowed egress behavior, access to the endpoint might be affected. In this case, you need to create a specific egress allow firewall rule or policy to permit traffic to the internal destination IP address of the endpoint.
In most scenarios, it is recommended that you use private endpoint connection over VPC peering. However, in the following scenarios, you should use VPC peering instead of private endpoint connection:
- You are using a TiCDC cluster to replicate data from a source TiDB cluster to a target TiDB cluster across regions, to get high availability. Currently, private endpoint does not support cross-region connection.
- You are using a TiCDC cluster to replicate data to a downstream cluster (such as Amazon Aurora, MySQL, and Kafka) but you cannot maintain the endpoint service of the downstream on your own.
Set up a private endpoint with Google Cloud Private Service Connect
To connect to your TiDB Dedicated cluster via a private endpoint, complete the prerequisites and follow these steps:
- Choose a TiDB cluster
- Provide the information for creating an endpoint
- Accept endpoint access
- Connect to your TiDB cluster
If you have multiple clusters, you need to repeat these steps for each cluster that you want to connect to using Google Cloud Private Service Connect.
Prerequisites
Before you begin to create an endpoint:
Enable the following APIs in your Google Cloud project:
Prepare the following IAM roles with the permissions needed to create an endpoint.
- Tasks:
- Create an endpoint
- Automatically or manually configure DNS entries for an endpoint
- Required IAM roles:
- Compute Network Admin (roles/compute.networkAdmin)
- Service Directory Editor (roles/servicedirectory.editor)
- Tasks:
Perform the following steps to go to the Google Cloud Private Endpoint page:
- Log in to the TiDB Cloud console.
- Click in the lower-left corner, switch to the target project if you have multiple projects, and then click Project Settings.
- On the Project Settings page of your project, click Network Access in the left navigation pane, and click the Private Endpoint tab.
- Click Create Private Endpoint in the upper-right corner, and then select Google Cloud Private Endpoint.
Step 1. Choose a TiDB cluster
Click the drop-down list and choose an available TiDB Dedicated cluster.
You can select a cluster with any of the following statuses:
- Available
- Restoring
- Modifying
- Importing
Step 2. Provide the information for creating an endpoint
- Provide the following information to generate the command for private endpoint creation:
- Google Cloud Project ID: the Project ID associated with your Google Cloud account. You can find the ID on the Google Cloud Dashboard page.
- Google Cloud VPC Name: the name of the VPC in your specified project. You can find it on the Google Cloud VPC networks page.
- Google Cloud Subnet Name: the name of the subnet in the specified VPC. You can find it on the VPC network details page.
- Private Service Connect Endpoint Name: enter a unique name for the private endpoint that will be created.
- After entering the information, click Generate Command.
- Copy the command.
- Go to Google Cloud Shell to execute the command.
Step 3. Accept endpoint access
After executing the command in Google Cloud Shell successfully, go back to the TiDB Cloud console and then click Accept Endpoint Access.
If you see an error not received connection request from endpoint, make sure that you have copied the command correctly and successfully executed it in your Google Cloud Shell.
Step 4. Connect to your TiDB cluster
After you have accepted the endpoint connection, take the following steps to connect to your TiDB cluster:
- On the Clusters page, click ... in the Action column.
- Click Connect. A connection dialog is displayed.
- Select the Private Endpoint tab. The private endpoint you just created is displayed. Copy the command to connect to the TiDB cluster.
Private endpoint status reference
When you use private endpoint connections, the statuses of private endpoints or private endpoint services are displayed on the Private Endpoint page.
The possible statuses of a private endpoint are explained as follows:
- Pending: waiting for processing.
- Active: your private endpoint is ready to use. You cannot edit the private endpoint of this status.
- Deleting: the private endpoint is being deleted.
- Failed: the private endpoint creation fails. You can click Edit of that row to retry the creation.
The possible statuses of a private endpoint service are explained as follows:
- Creating: the endpoint service is being created, which takes 3 to 5 minutes.
- Active: the endpoint service is created, no matter whether the private endpoint is created or not.
Troubleshooting
TiDB Cloud fails to create an endpoint service. What should I do?
The endpoint service is created automatically after you open the Create Google Cloud Private Endpoint page and choose the TiDB cluster. If it shows as failed or remains in the Creating state for a long time, submit a support ticket for assistance.
Fail to create an endpoint in Google Cloud. What should I do?
To troubleshoot the issue, you need to review the error message returned by Google Cloud Shell after you execute the private endpoint creation command. If it is a permission-related error, you must grant the necessary permissions before retrying.
I cancelled some actions. What should I do to handle cancellation before accepting endpoint access?
Unsaved drafts of cancelled actions will not be retained or displayed. You need to repeat each step when creating a new private endpoint in the TiDB Cloud console next time.
If you have already executed the command to create a private endpoint in Google Cloud Shell, you need to manually delete the corresponding endpoint in the Google Cloud console.
Why can't I see the endpoints generated by directly copying the service attachment in the TiDB Cloud console?
In the TiDB Cloud console, you can only view endpoints that are created through the command generated on the Create Google Cloud Private Endpoint page.
However, endpoints generated by directly copying the service attachment (that is, not created through the command generated in the TiDB Cloud console) are not displayed in the TiDB Cloud console.